
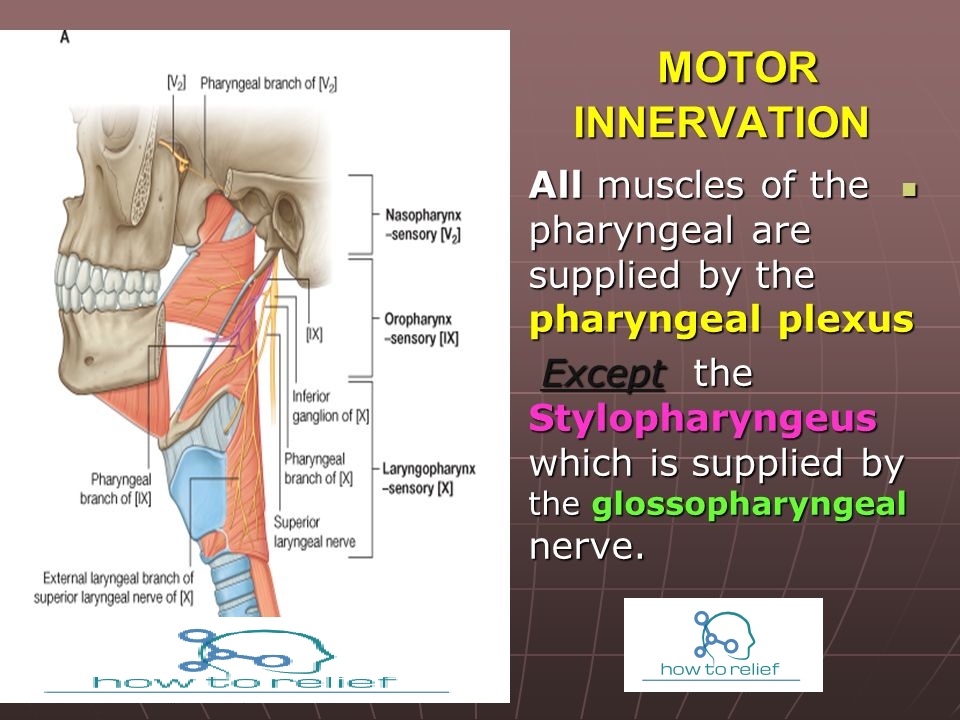
Other complication includes gurgling, aspiration, foul breath, and neck mass. This structure is called Zenker diverticulum, and it can cause an accumulation of food into the pouch and can lead to dysphagia. If there is incoordination of contraction and relaxation of these two muscles, intrapharyngeal pressure can rise and form a diverticulum between the weak spot of the two muscles. The thyropharyngeus muscle is superior to the cricopharyngeus muscle, and during normal swallowing, the thyropharyngeus contracts while the cricopharyngeus relaxes to propel the food into the esophagus. The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle subdivides into the thyropharyngeus and cricopharyngeus muscle. These longitudinal muscles work to elevate the pharynx and larynx superiorly during swallowing. As previously mentioned, this muscle is different from the other pharyngeal muscle in that it is the only muscle innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve. When the stylopharyngeus muscle contracts, it elevates the pharynx and larynx. The stylopharyngeus muscle origin is from the styloid process of the temporal bone and it inserts into the posterior thyroid cartilage as well as merging with muscle fibers of the palatopharyngeal muscle. This muscle contracts to elevate the pharynx superiorly as well as opening the auditory tube when swallowing. The salpingopharyngeus muscle originates from the inferior auditory tube and inserts into the palatopharyngeus muscle. When the palatopharyngeus muscle contracts, it elevates the pharynx superiorly. The palatopharyngeus muscle originates from the posterior hard palate, the palatine aponeurosis, and inserts into the thyroid cartilage. The inner longitudinal layer consists of the palatopharyngeus, salpingopharyngeus, and stylopharyngeus muscles. These constrictor muscles work together and contract to push food after swallowing to propel it from the oral cavity into the esophagus. When the inferior constrictors contract, they constrict the lower portion of the pharynx.

The cricopharyngeus muscle originates from the cricoid cartilage and blends into the esophageal muscle. The thyropharyngeus muscle originates from the thyroid cartilage and inserts into the median pharyngeal raphe. The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle further divides into two muscles, the thyropharyngeus, and the cricopharyngeus muscle. The middle constrictor muscle contracts to constrict the middle portion of the pharynx. The middle constrictor inserts into the median pharyngeal raphe as well as blending in with fibers of the superior and inferior constrictors. The middle constrictor muscle originates from the greater and lesser horn of the hyoid bone and stylohyoid ligament. When the superior constrictor muscle contracts, it constricts the upper portion of the pharynx. The pharyngeal raphe is a midline tendinous seam where the constrictor muscles meet.

This superior constrictor muscle inserts into the base of the skull at the pharyngeal tubercle and the pharyngeal raphe. The superior constrictor muscle originates from the pterygoid process, posterior end of the mylohyoid line of mandible, and the pterygomandibular ligament/raphe. The outer circular layer consists of the superior, middle, and inferior constrictor muscles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
